Big data describes large volumes of data which can either be structured or unstructured that inundates a business on a day-to-day basis. The term big data represents the unmanageable large datasets. It is not what organisations do with the data but the insights that can be analysed from the data which lead to better decisions and strategic business moves. Big data is the major asset of today’s tech world and when the Coronavirus pandemic hit the economy and workspace it pushed everyone to work remotely. In that instance, the big data stood as a compliment and it paved the way and accelerated the working strategy without a pause.
According to Mezmo, the big data trends are strongly connected to augmented analytics, cloud optimization, continuous intelligence, edge computing, and many other disciplines in the tech world which significantly improve the way we work with big data. It is prudent to note that big data has been a hot topic for years now as it is continuously changing the way companies do business and take advantage of all the data they process. This has made big data analytics a much quicker, more convenient and cheaper way to deal with data that flows within a company. Thanks to big data, companies are now working smarter, faster and more efficient.
What is big data?
According to TechTarget, big data is a combination of structured, semi-structured and unstructured data collected by companies that can be mined for information and used in machine learning projects, predictive modelling and other advanced analytics applications. It is often characterised by the 3Vs, first identified by Doug Laney in 2001, which are:
- The volume of data in many environments
- The wide variety of data types stored in big data systems
- The velocity at which the data is generated, collected and processed
However, several other Vs have been added to different descriptions of big data and these include:
- Veracity
- Value
- Variability
- Virality
- Visualisation
- Viscosity
It is no secret that lately the term ‘Big data’ has been under the limelight but not many people really know and understand what it is. Several institutions including governments, businesses, health care providers, academic institutions and financial service providers are all leveraging on the big data to enhance business prospects along with an improved customer experience. IBM maintains that businesses around the world generate nearly 2.5 quintillion bytes of data daily. Almost 90% of the global data has been produced in the last 2 years alone. The definition by Gartner clearly answers what big data is and it is as follows:
\"Big data is high-volume, velocity, and variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing for enhanced insight and decision making.\"
Gartner
There are certain tenets of big data that can also help to clearly define big data and these include:
- It refers to a massive or very enormous amount of data that keeps on growing exponentially with time
- It is so voluminous that it cannot be processed or analysed using conventional data processing techniques
- It includes data mining, data storage, data analysis, data sharing and data visualisation
- The term is an all comprehensive one including data, data frameworks along with the tools and techniques used to process and analyse the data
Characteristics of big data
Advertisment
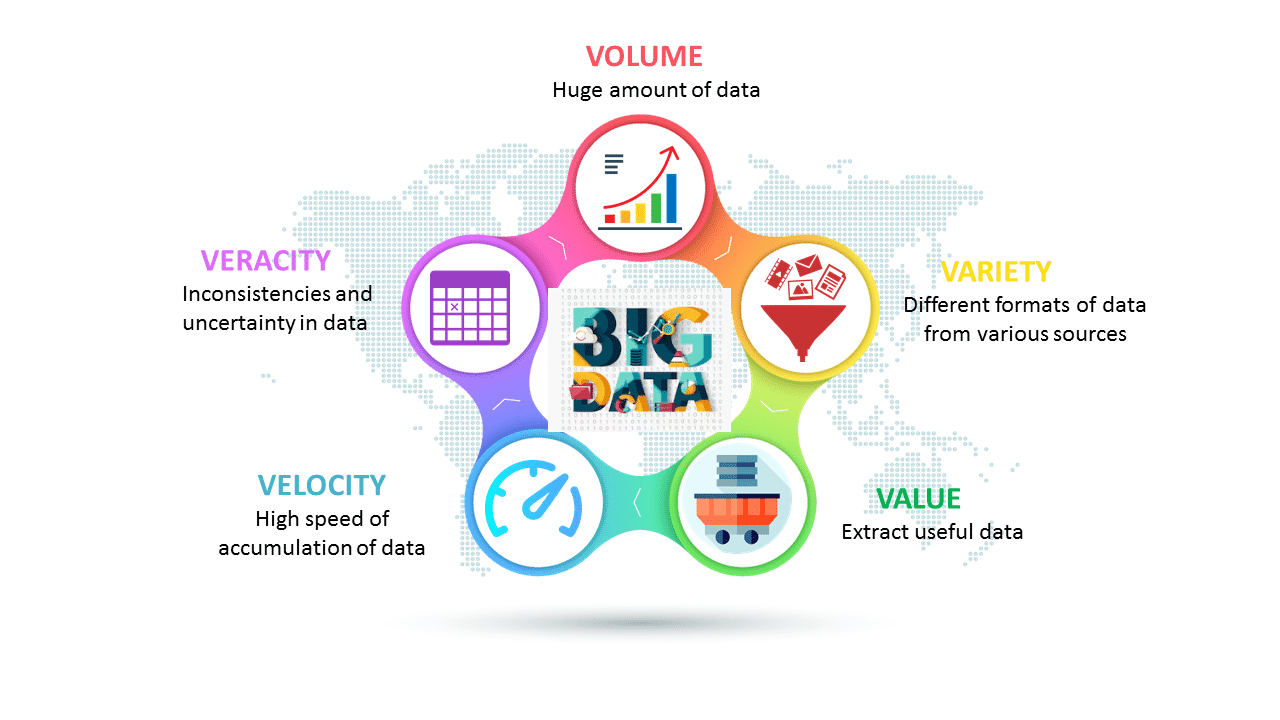
The act of gathering and storing large amounts of information for eventual analysis is ages old even though big data is a relatively new term. The concept gained momentum in the early 2000s when the industry analyst Doug Laney articulated the now-mainstream definition of big data using the Vs. Each of the Vs or the characteristics of big data can be further explained as follows:
Volume
Most companies collect data from a variety of sources which include business transactions, social media and information from sensor or machine-to-machine data. This has been made possible with the new technologies such as Hadoop which ease the burden of storing the data. The size of the data plays a very crucial role in determining the value out of the data. As the term big data itself is already related to a size which is enormous, hence a particular data can actually be considered as a big data or not which is dependent upon volume of data.
Velocity
It is important that data streams in an unprecedented speed must be dealt with in v timely manner. RFID tags, sensors and smart metering are driving the need to deal with torrents of data in near real-time. The term velocity refers to speed just as it is used in physics but in this case it is the speed of generation of data. How fast the data is generated and processed to meet the demands, determine its real potential in the data. Big data velocity deals with the speed at which data flows in from sources like business processes, application logs, networks and social media sites, sensors, mobile devices etc. The flow of data is massive and continuous.
Variety
It is common practice that data comes in all types of formats from structured datasets, numeric data in traditional databases to unstructured text documents, emails, video, audio, stock ticker and unstructured. The variety of unstructured data poses certain issues for storage, mining and analysing data.
Veracity
Veracity refers to the quality of data or rather the degree of certainty in the data. Since data comes from so many different sources, it is difficult to link, match, cleanse and transform data across systems. Businesses need to connect and correlate relationships, hierarchies and multiple data linkages. Otherwise, their data can quickly spiral out of control. Bad data leads to inaccurate analysis and may undermine the value of business analytics because it can cause executives to mistrust data as a whole.
Value
Not all data collected has real or actual business value and the use of inaccurate data can weaken the insights provided by analytics applications. It is critical that organisations employ practices such as data cleansing and confirm that data relates to relevant business issues before they use it in a big analytics project.
Variability
As an addition to the increasing velocities and varieties of data, data flows are unpredictable that is they are changing often and varying greatly. It is challenging but businesses need to know when something is trending in social media and how to manage daily, seasonal and event-triggered peak data loads. Variability often applies to sets of big data which are less consistent than conventional transaction data and may have multiple meanings or be formatted in different ways from one data source to another. These factors can complicate efforts to process and analyse the data.
Virality
This describes how quickly information gets dispersed across people to people networks. Virality measures how quickly data is spread and shared to each unique node. Time is a determinant factor along with the rate of spread.
Viscosity
Viscosity measures the resistance to flow in the volume of data. This resistance can come from different data sources, friction from integration flow rates and processing reuired to turn the data into insights. Technologies to deal with viscosity include improved streaming, agile integration bus and complex event processing. This is all about whether or not the big data sticks with you or does it call for action.
Visualisation
Big data visualisation calls back to memory the old saying of a picture is worth a thousand words. This is because, at a glance, the image can convey what is going on more quickly and efficiently. However, big data visualisation techniques exploit this fact as they are all about turning data into pictures by presenting data in pictorial or graphical format. This makes it easy for the decision makers to take vast amounts of data at a glance to see what is going on and what is it that the data has to say. They can make sense at a glance of the visuals and this triggers decisions.
Big data examples
Big data comes from myriad different sources such as business transaction systems, customer databases, medical records, internet clickstream logs, mobile applications, social networks, scientific research repositories, machine-generated data and real-time data sensors used in the internet of things environments. It can serve to deliver benefits in various areas and some of them are as follows:
Big data in education
Big data is playing a very important role in education and the following is some of the fields in the education industry that it has transformed and motivated very significant changes:
- Customised and dynamic learning programs
- Reframing course material
- Grading systems
- Career prediction
Big data in insurance
The insurance industry is important both for individuals and businesses. It holds a significant place because it supports people during times of adversities and uncertainties. The data collected from these sources are varying formats and change at tremendous speeds. The insurance industry can use the big data feature to pounce on when they gather and collect information. Determining the customer experience and making customers the centre of a business’s attraction is of prime importance. Big data can also be used for reducing fraud and it is highly effective in doing so.
Threat mapping can also be conducted when an insurance agency sells insurance, they would want to be aware of all possibilities of things going unfavourable with their customer making them file a claim.
Big data in government
Proper analysis of the enormous data that governments come across daily helps the governments in endless ways which also include welfare schemes and cyber security. It has an enormous impact locally, nationally and globally. Given the vast number of complex issues the governments have to go through each day, big data will assist them to make sense out of all the information they receive and be able to make vital decisions that affect millions of people.
Big data in banks
In the banking sector, the volume of data skyrockets every second. This data is expected to rise by 700% by 2020, according to the GDC prognosis. Big data research and analysis can help identify:
- The unfair use of credit cards
- Misuse of cards for debit
- Credit threat care for Venture
- Clearness of Business
- Alteration of consumer statistics
- Laundering Money
- Mitigation of Risk
Big data in product development
Big data is used by companies such as Netflix and Procter & Gamble to anticipate client demand. By classifying key attributes of past and current products or services and modeling the relationship between those attributes and the commercial performance of the offerings, they create predictive models for new products and services. In addition, to design, develop, and introduce new products, P&G uses data and analytics from focus groups, social media, test markets, and early store rollouts.
Big data in predictive maintenance
Structured data such as the year, manufacture, and model of equipment, as well as unstructured data covering millions of log entries, sensor data, error messages, and engine temperature, may be deeply buried in factors that can forecast mechanical failures. Through analysing these signs of possible issues before the problems arise, companies can more cost-effectively deploy repairs and optimize the uptime of parts and equipment.
Big data in customer experience
The race is on for buyers. More than ever before, a better picture of the consumer experience is now possible. In order to optimize the interaction experience and enhance the value delivered, big data helps you to collect data from social media, site visits, call logs, and other sources. Start to deliver customized deals, reduce consumer satisfaction, and proactively manage problems.
Big data in fraud and compliance
It's not just a few rogue hackers when it comes to security; you're up against whole teams of experts. Security conditions and compliance standards are continually changing. Big data allows you to detect data trends that reveal manipulation and aggregate vast amounts of data to make regulatory reporting much easier.
Big data in machine learning
Machine learning right now is a hot subject. And one of the reasons for that is data, especially big data. We are now in a position to teach machines rather than program them. That is made possible by the accessibility of big data to train machine learning models.
Big data in operational efficiency
The news may not always be about operational performance, but it's an environment in which big data has the most effects. You can track and compare production, consumer reviews and returns, and other variables with Big data to reduce outages and predict future demands. Big data can also be used in line with real business demand to enhance decision-making.
Big data in drive innovation
By researching interdependencies between individuals, organizations, agencies, and processes, and then identifying new ways to use those insights, big data will help you innovate. To enhance decisions on financial and planning considerations, use data insights. Examine patterns and what new goods and services consumers want to offer. Enforce dynamic pricing. Infinite possibilities exist.
Types of big data
There are three types of big data and there are:
- Structured
- Unstructured
- Semi-structured
Structured
Structured big data is any data that can be stored, accessed and processed in a fixed format. Overtime, computer science experts managed to develop techniques for working with such kind of data easily and successfully. The following is an example of structured data of employees in an employee table in a database.
Employee_ID
Employee_Name
Gender
Department
Salary
2365
Jane Doe
Female
Finance
65,000
3398
John Doe
Male
Marketing
55,000
Unstructured
This is any data with an unknown form or that lacks any specific form or the structure is classified as unstructured data. In addition to the unstructured data being huge, it also possess multiple challenges in terms of its processing for deriving value out of it. This makes it very difficult and time-consuming to process and analyse. A good example is a heterogeneous data source containing a combination of simple text files, images, videos etc. An email is also a good example of unstructured big data.
Semi-structured
Semi-structure big data can contain both the structured and unstructured data. It refers to the data that although it has not been classified under a particular repository yet it contains vital information or tags that segregate individual elements within the data. The following is an example of semi-structured data that is stored in an XML file:
Jane DoeFemale>35John DoeMale>55
Benefits of big data
The ability to process big data brings in multiple benefits such as:
- Businesses can utilise outside intelligence while making decisions
- Improved customer services through insights obtained from harnessing data from social media and other platforms
- Early identification of risk to the product/service (if any)
- Better operational efficiency
- It makes it possible to gain more complete answers because there is more information
- More answers mean more confidence in the data when solving problems
- Ability to predict outcomes accurately using predictive analysis thereby allowing businesses to make better decisions while simultaneously optimising their operational efficiencies and reducing risks
- Being accurate by combining data from relevant sources to produce highly actionable insights
- Generate more sales leads thus a boost in revenue as businesses can use big data to understand how well their products/services are doing in the market and how the customers are responding to them
- Ability to stay ahead of competitors by screening the market and get insights that allows the businesses to learn customer behaviours to understand the customer trends and provide highly personalised experiences to them
Challenges of big data
There are several challenges that big data also imposes besides the processing capacity and cost issues. Designing a big data architecture is another challenge for users. Big data systems must be tailored to an organisations particular needs, a DIY undertaking that requires IT teams and application developers to piece together a set of tools from all the available technologies. Deploying and managing big data systems also require new skills compared to the ones possessed by database administrators and developers focused on relational software. Both of the above mentioned issues can be managed by cloud services but IT managers need to keep a close eye on the cloud usage to make sure costs don’t get out of hand.
Migrating on-premises data sets and processing workloads to the cloud is often a complex process for many businesses. Another challenge is making the data in the big data systems accessible to data scientists and other analysts especially in distributed environments that include a mix of different platforms and data stores. To help and ensure analysts find relevant data, IT and analytics teams are increasingly working to build data catalogues that incorporate metadata management and data lineage functions. Data quality and data governance also need to be priorities to ensure that sets of big data are clean, consistent and used properly.
Importance of big data
The importance of big data is not centred on how much data one has but rather what one does with the data. When combined big data with high-powered analytics, a company can establish a lot. The following are some of the importance of big data:
- Big data is well known for its efficiencies and these include:
- Cost reduction
- Time reduction
- New product development through stored data and optimised offerings
- Smart and accurate decision making
- Understanding the market conditions through analysis of the big data
- Control online reputations through sentiment analysis
- Boost customer acquisition and retention by learning what the customer wants
- Solve advertisers problem and offer marketing insights
- Acts as a driver of innovations and product development
- Determine root causes of failures, issues and defects in near real-time
- Generating coupons at the point of sale based on the customers buying habits
- Recalculating entire risk portfolios in minutes
- Detecting fraudulent behaviour before it affects the company
Big data and analytics
Big data analytics is the use of advanced analytical techniques toward very broad, complex collections of big data, including structured, semi-structured and unstructured data from various sources and from terabytes to zettabytes in various sizes. Ultimately, big data analytics will fuel better and quicker decision-making modeling and forecasting of future performance and improved business intelligence. Consider open source applications such as Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark and the entire Hadoop ecosystem as cost-effective, scalable data processing and storage tools designed to manage the amount of data being generated today as you develop your big data solution.
Big data tools
Source
Uber
Uber is one of the world's largest taxi service providers. It leverages customer information to track and recognize the users' most common and most used services. Uber uses data analytics to evaluate the consumption habits of consumers to assess which services can be given more attention and value once this information is collected. Besides this in another special way, Uber uses Big data. Uber monitors the demand and availability of its services closely and modifies the cab tariffs accordingly. It's the mechanism of surge pricing that works something like this, assume that when you're in a rush, and you need to book a cab from a crowded spot, Uber will charge you twice the usual price!
Netflix
Netflix is one of the most common sites for streaming on-demand online video content used by individuals around the world. A big proponent of the recommendation engine is Netflix. To understand the unique needs, tastes, and taste habits of consumers, it collects customer data. It then uses this information to predict what individual users would want and create lists of suggestions for them for customized content. Netflix has become so vast today that it is now producing original user content. Data is the hidden ingredient that drives both its engines of suggestion and new decisions on content. Titles that users stream, user reviews, genres preferred, and how often users stop playing, to name a few, are the most significant data points used by Netflix. The three main parts of the data structure used by Netflix are Hadoop, Hive, and Pig.
Procter & Gamble
For ages now, Procter & Gamble has been among us. Nevertheless, despite being a "old" entity, P&G is nowhere close to old in its ways. Recognizing Big data's promise, in each of its business divisions around the world, P&G began incorporating Big data tools and technologies. The key focus of the business behind the use of Big data was to use real-time insights to drive smarter decision making. To achieve this goal, P&G began gathering large quantities of structured and unstructured data, both from company archives and online sources, through R&D, supply chain, customer-facing operations and customer interactions. In order to allow managers to access the latest industry data and analytics, the global brand has also established Big data systems and processes.
IRS
Yes, government departments don't shy away from using big data, either. Big data is actively used by the US Internal Revenue Service to deter identity theft, fraud, and untimely payments. In order to ensure and enforce compliance with tax rules and regulations, the IRS also harnesses the power of Big data. As of now the IRS, especially in the case of identity theft, has successfully avoided fraud and scams involving billions of dollars. It has also recovered over US$ 2 billion in the last three years.
For some kinds of workloads, many companies embrace big data and use it to complement their current research and business resources to optimize revenue. Even if big data doesn't fit all working types, gathering and storing them at all costs is still important. It may not be now but the data stored will one day turn into an invaluable asset.
Kudzai Derera is a Consultant at Industrial Psychology Consultants (Pvt) Ltd, a management and human resources consulting firm.
LinkedIn: https://zw.linkedin.com/in/kudzaiderera
Phone: +263 242 481946-48/481950
Email: kudzai@ipcconsultants.com
Main Website: www.ipcconsultants.com
