A broad variety of new occupations are likely to signal the future of work, much of which we can barely conceive of today. In a fresh study carried out by the online learning provider Udemy, this focus on soft skills also emerged. They analyzed the courses that businesses need workers to take today to try to gauge a deeper understanding of where skill shortages occur. According to Udemy's 2020 Workplace Learning Trends Report, the most critical soft skill for job success was rated as having a growth mindset or the ability to continue learning to adapt to change. This analysis was done using the user data from Udemy’s for Business service which provides many course packages and is used by more than 4,000 businesses as a resource for staff training.
One study by McKinsey & Company suggested that as many as 800 million global employees could lose their jobs to robots by 2030. To remove jobs that can easily be accomplished by automation and computers, as digital technology threatens, workers and work-seekers are increasingly focusing on cultivating a growth mindset. The second issue of the 'Future of Jobs' report from the World Economic Forum forecasts the loss of 75 million jobs by 2025. But it is also estimated that 133 million jobs will be generated thanks to the digital revolution. The World Economic Forum advises us, with projections for 2022, on the critical skills to grow today and tomorrow! They are soft skills. But what exactly are soft skills?
What are soft skills?
Soft skills are characteristics and actions of personalities. Soft skills are not about the expertise one possesses, but rather the attitudes he/she exhibits in various environments, unlike hard skills. They are any ability or attribute that can be identified as a feature or habit of a personality. More basic types of soft skills are interpersonal skills and communication skills that many employers search for in work applicants. In a recent survey of 1,000 hiring managers, the managers were asked to list the most important attributes of top performers in their companies and the following came out as the top 5:
- Problem-solving
- Effective communication skills
- Self-direction
- Drive
- Adaptability/Flexibility
However, according to LinkedIn research, the most in-demand soft skills are:
- Communication
- Organization
- Teamwork
- Critical thinking
- Social skills
- Creativity
- Interpersonal communication
- Adaptability
Soft skills are more related to emotional intelligence and are natural skills that help people connect well with others. They are also typically not the kind of talents that can be used in a segment of resume skills. Rather, by developing an accomplishment-oriented professional experience segment, one can highlight his/her soft skills. They are useful across all industries and job types when compared to hard skills. On the other hand, hard skills are usually job-specific skills that are learned through schooling or training. The difference between hard skills vs soft skills are as follows:
Related: Emotional Intelligence Leader
The determining factor for employers in today's work market sometimes comes down to a struggle between various candidates' hard vs. soft skills. A survey provided by SMB World found that nearly 72% of CEOs agree that soft skills are more important than hard skills for their company's success. That being said, to make the complete package an employer needs, soft skills and hard skills should complement each other. For instance, to perform their job well, a graphic designer requires both soft creativity skills and hard adobe Photoshop skills. The following image shows examples of hard skills versus examples of soft skills, clearly showing their differences:

Source: Indeed
Related: Hard Skill Vs Soft Skill
List of soft skills
As we have explored that a McKinsey study forecasts that by 2030, up to 30% of the hours worked globally will be automated. The Future of Work report from the World Economic Forum estimates that 5 million employees will no longer exist before 2020 as human employees are replaced by artificial intelligence and robotics. However, due to this move, more than 2 million jobs will also be created and special human abilities will become more important. These human skills are vital now and in the future work. The following is a list of the soft skills which are important now and in future work.
These soft skills are required in the workplace and some of them are listed with their examples
1. Growth mindset: The capacity to constantly learn and the ability to adapt to change
2. Creativity: Developing new ideas, introducing new strategies to solve current issues. Types of creative skills include:
- Divergent thinking
- Inspiration
- Imagination
- Reframing
- Mind mapping
- Insight
- Innovation
- Experimenting
- Questioning
- Design
3. Focus mastery: Harnessing emphasis to make better short- and long-term choices
4. Innovation: Improving an established system, concept, procedure or approach for achieving the desired result
5. Communication: Interpreting data by speaking, listening, and observing. Some examples include:
- Clarity
- Confidence
- Respect
- Empathy
- Listening
- Verbal communication
- Non-verbal communication
- Written communication
- Constructive feedback
- Friendliness
6. Storytelling: Organizing points of view and knowledge into a comprehensive, cohesive narrative
7. Culture awareness: Ability to communicate, collaborate and build substantive relationships effectively with people within the company with different cultural backgrounds
8. Critical thinking: Objective review and assessment to shape a decision on a subject
9. Leadership: Providing guidelines inside an organization. Leadership skills include:
- Empathy
- Selflessness
- Agility
- Listening
- Humility
- Cultural intelligence
- Authenticity
- Versatility
- Generosity
- Trust
11. Emotional intelligence: Regulation, expression, and observation of interpersonal interactions between individuals in the workplace
12. Integrity: Honest, ethical, high morals, has personal values, does what’s right
13. Dependability: The quality of being trustworthy and reliable
14. Open-mindedness
15. Teamwork: Cooperative One, gets along with others, agreeable, supportive, helpful, and collaborative. Some examples of teamwork-related skills include:
- Conflict management
- Delegation
- Listening
- Active listening
- Collaboration
- Cooperation
- Coordination
- Idea exchange
- Mediation
- Negotiating
16. Problem-solving: Solve issues quickly and effectively. Types of problem-solving skills include:
- Analysis
- Lateral thinking
- Logical reasoning
- Initiative
- Persistence
- Observation
- Persuasion
- Negotiation
- Brainstorming
- Decision making
17. Adaptability: Quickly respond to changing trends, innovation, destabilization, industry shifts, and so forth. Some examples include:
- Curiosity
- Self-management
- Decision-making
- Calmness
- Optimism
- Open-mindedness
- Analysis
- Self-confidence
- Organization
- Self-motivation
18. Organization: Ability in the workplace to act efficiently. On the job, such skills and characteristics as preparedness and attention to detail can manifest themselves as the ability to manage a large workload or execute a complex project within an established time frame.
19. Empathy: One who understands and shares the feelings of others
20. Courtesy: Has manners, etiquette, business etiquette, gracious, says please and thank you, respectful
21. Flexibility: Adaptability, willing to change, lifelong learner, accepts new things, adjusts, teachable
22. Work ethic: One who is hard working, willing to work, loyal, initiative, self-motivated, on time, good attendance. Soft skills examples related to work ethic include:
- Integrity
- Responsibility
- Discipline
- Initiative
- Dependability
- Commitment
- Self-motivated
- Professionalism
- Teamwork
- Time-management
23. Interpersonal skills: A nice, personable, sense of humor, friendly, nurturing, empathetic, self-control, patient, sociability, warmth, and social skills. Examples include:
- Empathy
- Humor
- Mentoring
- Networking
- Sensitivity
- Patience
- Tolerance
- Public speaking
- Positive reinforcement
- Diplomacy
24. Positive attitude: Optimistic, enthusiastic, encouraging, happy, confident
25. Professionalism: A businesslike, well-dressed, appearance, poised
26. Responsibility: Accountable, reliable, gets the job done, resourceful, self-disciplined, wants to do well, conscientious, common sense
27. Conflict resolution: A way for two or more parties to find a peaceful solution to a disagreement among them
28. Time management: Being able to manage time effectively in the face of so many competing demands is vital. Some time management skills are:
- Goal setting Resume Sample for a Project Manager
- Prioritizing
- Self-starter
- Planning
- Decision making
- Focus
- Delegation
- Stress management
- Coping
- Organization
29. Stress management: Being able to cope with stress
30. Customer service/Service orientation: Providing timely, attentive, upbeat service to a customer, and making sure their needs are met in a manner that reflects positively on the company or business
31. Personal productivity: Being able to get the most from a working day, blocking out the numerous distractions vying for one’s attention.
32. Change management: It is ever-present, yet equally often flunked. Being able to change effectively is a skill that will rarely go out of demand.
33. Strategic thinking: Give meaning and derive a purpose and strategy from all the information using automation tools, such as data-based algorithms etc.
34. Collaboration: The ability to work effectively in team environments ensures that everyone is contributing something of value to the table in a way that also promotes peace and healthy relationships in the workplace.
35. Confidence: It is apparent in everything you do and says – your appearance, your behaviour, even the work you submit and the simple ways in which you hold yourself
36. Decision making: The ability of humans to go beyond the capabilities of tech, making critical decisions, and brainstorming new and innovative solutions
37. Analytical thinking: Ability to observe and research a problem or topic to develop more complex ideas about it
38. Social influence: How individuals change their behavior to meet the demands of a social environment
39. Curiosity: persistent and stays motivated in his/her quest to discover solutions for any problems they encounter
40. Negotiation: Ability to reach a decision which makes all parties happy, even if there is compromise and you don't get exactly what you set out to get
41. People management: Human leadership and management will still be important in the future as it requires strong interpersonal skills and leadership skills
42. Research: Help the company develop new products or services, identify the need and wants of their customers, improve what they do, keep up with changes in their industry and compete in their market
43. Active listening: Pay close attention to meeting presenters, offer up clarifying questions or responses, and refer back to notes in future discussions
44. Attention to detail: To be both thorough and accurate in work. Some skills related to attention to detail skills are:
- Critical observation accountant resume sample
- Listening
- Organization
- Scheduling
- Analysis
- Introspection
- Memory
- Acuity
- Recall
- Questioning
45. Self-motivation: People who are self-motivated get on by themselves
The importance of soft skills
94% of recruiters think that top-notch soft skills outweigh experience when it comes to promotion to leadership positions, according to Forbes. They are crucial to getting the work you want now and important for career advancement. Soft skills will become an ever more important differentiator for employers as automation grows. Any level of soft skills is required for most interactions with other individuals. You may be bargaining to win a new contract at a company, introducing your new concept to peers, networking for a new job, etc. Every day at work, we use soft skills, and learning these soft skills will help you win more business and speed up your career development.
A lack of soft skills, on the other hand, can limit your ability, or even be your business's downfall. You can run projects more smoothly, produce outcomes that satisfy others, and also positively affect your personal life by enhancing how you communicate with others by cultivating good leadership, delegation, teamwork, and communication skills. Soft skills such as communication are used outside of the workplace to create social groups and meet potential partners. You may be negotiating the price of renovating your new home or mentoring the children of your neighbors on the weekend. In both our professional and personal lives, soft skills are helpful. Here are some of the reasons why soft skills are important now and in the future of work:
1. Career progression and promotion
ICIMS Hiring Insights (2017) found that 94% of hiring professionals agree that an employee with stronger soft skills is more likely to be promoted to a leadership position than an employee with more years of experience but weaker soft skills. If you want to advance in your career, it is important to learn these skills as they will set you apart from others at the interview and on the job.
2 The modern workplace is interpersonal
In the modern workplace, skills like active listening, teamwork, proposing ideas, and engaging with colleagues are all highly regarded. Good soft skills maintain a positive, efficient and safe work climate, both of which are essential virtues in an increasingly competitive world for organizations.
3. Customers and clients demand soft skills
These days, customers have a large number of choices to buy from, purchased through the internet and smartphones. Convenience and low prices are easy to come by for these customers, so customer service is also what determines the option of using a specific company. Therefore, the ability to communicate with consumers at a human level is a critical factor in the performance of an organization.
4. The future workplace will rely on soft skills
A higher proportion of jobs relying on soft skills will result in automation and artificial intelligence. Technology advancements have caused activities that require hard skills to decline, making soft skills a crucial workplace differentiator. A Deloitte Access Economics report forecasts that by 2030, soft-skill-intensive employment will account for two-thirds of all workers. If the cost of robotics decreases and artificial intelligence efficiency increases, jobs such as production line employees will be automated. Traditional skills will be more important than ever, such as teamwork, communication, and critical thinking.
5. Soft skills are hard to automate
Soft skills such as emotional intelligence are difficult to automate, continuing from the previous stage, and are unlikely to be automated anytime soon. This means that, in the immediate future, they are likely to become more attractive. Soft skills, however, can be hard to teach and track changes. This is tackled by companies such as VirtualSpeech by using VR as a means of improving soft skills.
6 Soft skills are in high demand by recruiters
Soft skills in the workplace are in high demand. According to a Harvard student's 2017 report on the role of social skills in the labor market, as a share of the U.S. labor force, occupations requiring high levels of social interaction increased by nearly 12 percent.
7. Hard skills are useless without soft skills
Technical skills alone are not enough in most jobs to be truly effective. If they don't have the interpersonal skills needed to close deals and attract customers, a salesperson with an unrivalled knowledge of their product and market would have little success. A company manager must be able to listen to staff, have strong speaking abilities, and be able to think creatively. To make hard skills useful, all professions need at least some soft skills.
8. Soft skills are harder to learn
Hard abilities aren't inherently difficult to achieve. They can be taught quickly and, with time, can be mastered and refined. Soft skills are more difficult to acquire, since they have little to do with experience or competence, but are closely associated with the character of an individual. Strengthen your soft skills, it requires deliberate effort, diligent practice, and a dedication to self-development. On your CV, hard skills can look impressive, but soft skills are what will set you apart from the many applicants who have similar skills.
The advantages of having soft skills versus hard skills
Soft abilities include abilities for persons, relational abilities, character characteristics, organizational abilities, and transferable abilities. In the other hand, hard skills are job-specific technical skills. Your workforce's challenging skills come through schooling, certifications, training, and job experience. These skills can be taught, observable and able to be evaluated through examinations and practical tasks. Although hard skills are learned and perfected over time, it is much more challenging to acquire soft skills and difficult to assess and evaluate.
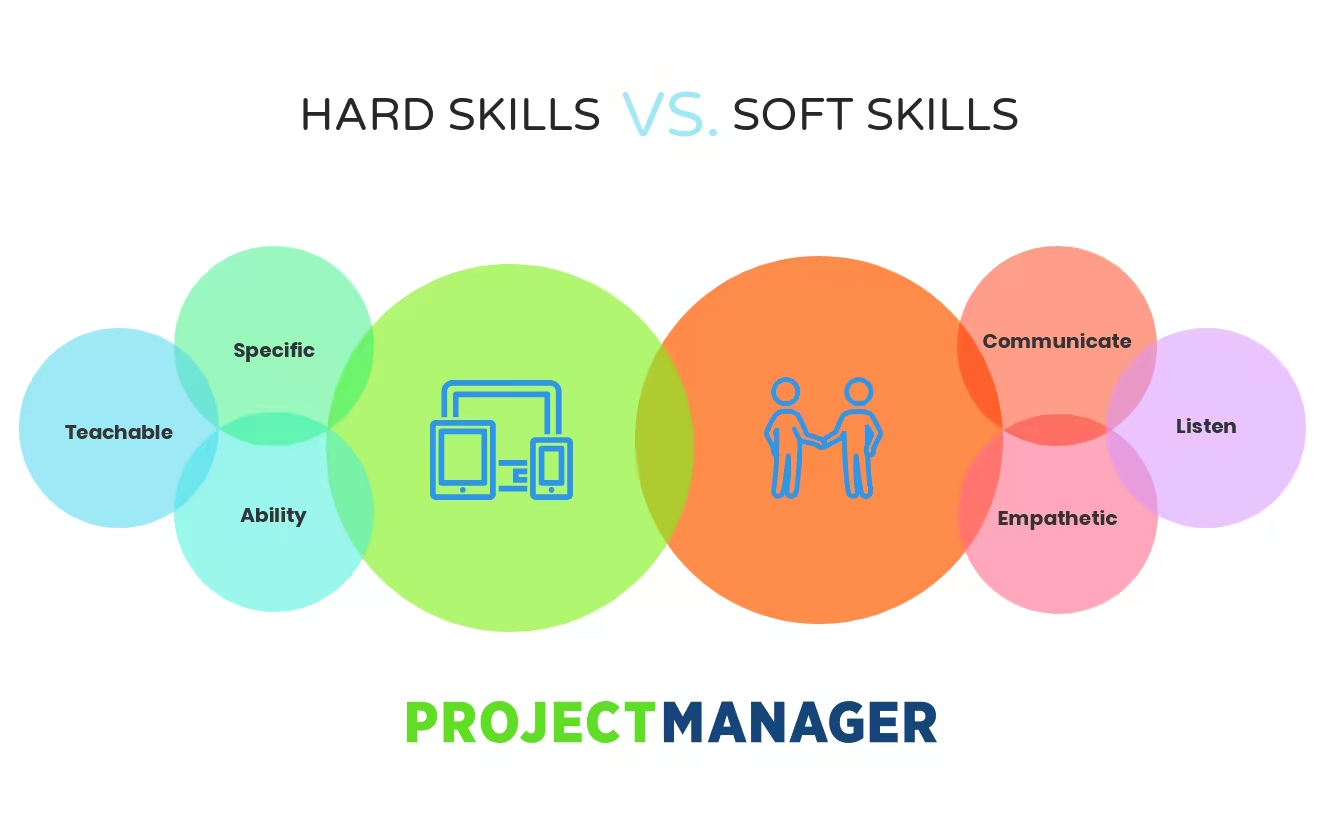
Source: Project Manager
Some of the advantages of having soft skills versus hard skills in the workplace include:
- Boost workplace productivity - improve employee performance and productivity across the board
- Reduce risks - help employees mitigate risks and solve problems on their own
- Improve customer service - is a spike in customer satisfaction
- Increase sales - employees can use their skills to engage with the customer/client on a personal level without blurring their professional boundaries
- Build a stronger team - employees become a cohesive unit because they're able to collaborate and respect each other's perspective
- More self-confidence, less stress - employees know they have what it takes to complete their job duties
- Improve employee retention - retain top talent because they have all the essential skills
Training people in soft skills
When we think about training in the workplace, soft skills can often be overlooked because they’re not as tangible as ‘hard skills’ like coding or advanced Excel skills. But developing soft skill training for employees is just as important as technical skills. One MIT Sloan study showed that in just eight months, a regulated, 12-month soft skills training trial in five separate factories yielded a 250% ROI. Their training in soft skills such as problem-solving and decision-making increased productivity, enhanced the performance of complex tasks, and strengthened employee engagement.
Stanford Research Institute International found that mastery of soft skills is the foundation for 75% of the long-term success in a given job position, and only 25% of that job success comes from technical skills. The outcomes from soft skills training are amazing, as you can see. But let's take a closer look at how it is functioning. There are a range of ways for employees to provide soft skills training. You can devote whole courses specifically to soft skills, or you can add suitable soft skill parts to the current content of the course. Consider using any of the options listed below, in terms of distribution methods:
1. Coaching/mentoring
If you know an employee who has a development need for a particular soft skill such as leadership, you may recommend taking a clear and tailored learning approach to a mentor or coach and tailoring. Usually, the workplace coaching process requires cooperation with the employee to identify, aim, and prepare for improved results. This is how it works: A coach determines the priorities, current skill sets, abilities, and, of course, shortcomings of the employee.
For instance, the employee learns that he/she is not good enough to communicate with the supervised workers, so a coach develops an improvement plan and provides him/her with a specific path to strengthen their communication skills. A teacher helps them and provides them with actionable input while an employee is on his way to implementing this technique. In imparting soft skills, such as communication and leadership, coaching / mentoring is particularly effective.
2. Live interactive workshops
You can schedule live workshops if you want to train an entire group of workers in a particular soft capacity. The best workshops have a clear, action-oriented focus and attempt to find answers to current issues in the field. Let's say that you want to train your customer service workers on how to handle customer disputes. You should carry out role-play scenarios right in the studio and play them out. Let a frustrated customer be the boss or learning and development agent and the staff will have to try to resolve the dispute. The teacher will be able to overcome skill differences based on their answers and point them in the right direction.
3. Peer (social) learning
Learning with other people is another successful and easy way of improving soft skills. Research has shown that there is a big correlation between workplace fun and informal learning. By developing work streams or small-scale projects that involve collaboration between colleagues at work, you can take advantage of this. Or, by using mobile apps and other resources, you can perform social learning online.
For instance, launch a peer forum where workers can discuss soft skills and how to reach their full potential in the workplace. To get peer-based input, they'll have a place to ask questions and share stories. An employee, for example, met a particularly unpleasant client who got on his or her nerves. He/she can share his/her experience on the forum, discuss it with colleagues, and get valuable advice for the future.
4. Online learning
Training your workers online makes sense in the current global climate. While training from home or other places in any unit, they may grow their soft skills. Some ready-made soft skills courses could be purchased from online learning sites like LinkedIn, Learning or Udemy. However, in fact, how can the workers consolidate their learned skills? And how are you going to verify that your peers got something useful out of the training?
Dialogue simulation is a perfect way to solve all problems and do soft skills training online that add real value. It is suitable for teaching business communication skills and other competencies that are similar. An online interaction that simulates an actual conversation with an individual, such as a client, another staff member, or a stakeholder, is a dialogue simulation. This is equivalent to the role-play scenarios we discussed when talking about live seminars, but sims are programmed and do not need other people to be involved.
As robots are on the rise, precisely what makes workers important is the very things that make us human. And while it might not be easy to acquire those soft skills, it's still absolutely possible! Designing the right learning approach and finding the best provider of solutions is what it takes. In the future workplace, technology will undoubtedly play an increasingly large role. Developing the soft skills of tomorrow in today's workplaces would give employees the ability to use the very skills that make them human to work, not against them, with their future AI colleagues.
Kudzai Derera is a Consultant at Industrial Psychology Consultants (Pvt) Ltd, a management and human resources consulting firm.
LinkedIn: https://zw.linkedin.com/in/kudsaiderera
Phone: +263 242 481946-48/481950
Email: kudsai@ipcconsultants.com
Main Website: www.ipcconsultants.com
.avif)
